Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Specialist in the Art of Healing!
Compationate Care for 28+ Years!
Button
Bunion and Hammertoe Expert
Dr. Reed has performed 2000+ bunion corrections!
Button
Wound Care Certified Specialist
Dr. Reed has Healed Over 3000 Ulers!

Ingrown Toenail Specialist
Innovative Nearly Painless Technique for Young to Old!
Button
Neuropathy Treatment Expert
We Reverse and Cure Neuropathic Pain!
Button
Fungal Toenail Expert
We create Beatuiful Toenails!
Button
Diabetic Foot Specialist!
Comprehensive Diabetic Foot Care!
Button
Sports Medicine Specialist
The Top Sports Injury Podiatrist!!
Button
Premier Custom Foot Orthotics
Optimizing Biomechanics and Performance!
Button
Neuropathy Cause & Treatment
Dr. Mark Reed has been using nitroglycerin patches since 1989 to improve blood flow and accelerate diabetic ulcer healing. Over 30 years, he developed a protocol that has reversed peripheral and autonomic neuropathy in over 3,000 patients while also preventing diabetic ulcers.
NEUROPATHY DEFINED
Diabetic neuropathy is a debilitating disorder that affects nearly 50% of patients with diabetes. In type 1 diabetes, neuropathy can present as a late finding after having the disease for more than five years, while in type 2 diabetes, it can be an early finding.
Types of Neuropathy:
- Peripheral Sensorimotor Neuropathy:
Symptoms: Pain, paresthesia, numbness, paralysis, cramping, nighttime loss of balance, and antalgic unstable gait.
Characteristics: Often described as having a "glove and stocking" distribution, as symptoms are present in areas covered by gloves or stockings.
2. Autonomic Neuropathy:
Symptoms: Dysfunction of cardiac, genitourinary, sudomotor, endocrine, and cerebral systems.
Cardiovascular Symptoms: Silent cardiac ischemia, orthostatic hypotension, vasomotor instability, exercise intolerance, fatigue, heart rate arrhythmia, syncope, dizziness, lightheadedness, and balance problems.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Dysphagia, gastroparesis, bladder dysfunction, bloating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and loss of bowel control.
Sudomotor Symptoms: Excessive sweating, pruritus, dry skin, limb hair loss, calluses, and reddened areas.
Endocrine Symptoms: Hypoglycemic unawareness.
Cerebral Symptoms: Sexual dysfunction, difficulty driving at night, depression, anxiety, sleep disorders, loss of food taste, decreased speech frequency, and cognitive memory loss.
Patients may present with only one type of diabetic neuropathy or may develop combinations of neuropathies, known as distal symmetric polyneuropathy. Distal symmetric polyneuropathy is the most common form, where numbness, tingling, and/or pain begins in the toes and slowly spreads into the foot and up the leg. Understanding the various types and symptoms of diabetic neuropathy is crucial for managing and treating this complex condition effectively.
DIABETIC PERIPHERAL & AUTONOMIC NEUROPATHY CAUSES
Diabetic neuropathy results from oxygen deprivation due to high blood glucose damaging small blood vessels and nerves. It can affect any part of the nervous system, not just the feet, and should be suspected in all type 2 diabetics and long-term type 1 diabetics.
Key Factors:
• Arterial Impact: High blood sugar causes swelling in arteriole muscles, restricting oxygen flow to tissues.
• Leukocyte Dysfunction: White blood cells, fibroblasts, and osteoblasts become immobile, leading to impaired healing and infection resistance.
• Loss of Pain Sensation: As nerves fail, patients lose protective pain responses, increasing the risk of ulcers and further complications.
PREVALANCE:
Peripheral neuropathy affects 60-70% of diabetics, but controlling blood glucose can lead to Diabetic Remission (A1C below 6). This prevents tissue damage and complications. However, some patients mistakenly consume high-glucose foods and offset them with insulin, leading to severe consequences like ulcers, dialysis, blindness, and amputations.
NON-DAIBETIC NEUROPATHY CAUSES:
Idiopathic Neuropathy: In many cases, patients may have no known cause for their neuropathy and are diagnosed with idiopathic peripheral neuropathy.
Diseases and Conditions:
- Alcoholism
- Kidney Failure
- Vitamin Deficiency: Particularly B12 and folate
- Shingles (Post-Herpetic Neuralgia)
- Fibromyalgia
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
- Autoimmune Diseases: Such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Guillain-Barre syndrome
- AIDS
- Syphilis
- Inherited Disorders: Such as amyloid polyneuropathy and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
- Exposure to Toxins:
- Heavy Metals: Including gold compounds, lead, arsenic, and mercury
- Organophosphate Pesticides
- Medications:
- Cancer Therapy Drugs: Such as Vincristine, Oncovin, and Vincasar
- Antibiotics: Such as metronidazole, Flagyl, and Isoniazid
Rare Causes:
- Neurofibromatosis
- Congenital Neuropathies: Including Fabry disease, Tangier disease, hereditary sensory autonomic neuropathy, and hereditary amyloidosis
- Anti-Cholesterol Statin Medications
- Peripheral Nerve Entrapments:
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome: In the ankle
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: In the hand
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY
Peripheral Neuropathy involes disorder of nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms include tingling, numbness, unusual sensations, weakness, or burning pain, often symmetrical in both hands and feet.
Autonomic Neuropathy: Symptoms vary depending on the nerve involved and can include numbness, different types of pain, weakness, or loss of balance. Affects bodily functions controlled by autonomic nerves, such as heart rate, digestion, and bowel and bladder control. Symptoms can include issues with blood pressure, voiding, stool passage (diarrhea or constipation), heart rate, and sweating. Cranial neuropathy involves cranial nerves, with ischemic optic neuropathy being a common cause due to loss of blood flow from the optic artery to the optic nerve.
Specific Nerve Involvement: Symptoms are limited to the distribution of the affected nerve.
WHAT TESTS DIAGNOSE PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY?
Medical History and Physical Examination: Essential first steps due to the diverse causes and presentations of peripheral neuropathy.
Specific Tests:
- Vibration and Semmes-Weinstein Monofilament Testing: Effective in diagnosing certain types of neuropathy, such as diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
Associated Conditions:
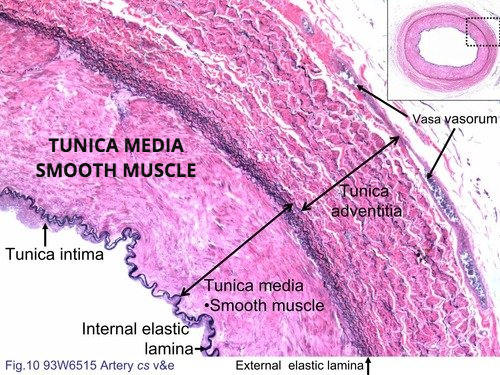
- Large Vessel Peripheral Vascular Disease:
- Affects 50% of type 2 diabetic patients with neuropathy.
- Involves narrowing or stenosis of large leg arteries.
- Important to evaluate large vessels by testing lower extremity pulses and ordering a doppler vascular lower extremity study if needed.
Importance of Early Diagnosis:
- Early Diagnosis and Intervention: Crucial for treating large vessel peripheral vascular disease to prevent foot ulcers and infections.
Additional Tests:
- Capillary Refill Time (CRT): Assesses small vessel vascular pathology.
- Sensory Testing: Integral for preventing new and recurrent foot ulcers in diabetic patients.
- Peripheral Arterial Doppler Testing: Ordered if a positive Semmes-Weinstein Monofilament test is noted.
- Blood Tests: For exposure to toxins.
- Electrodiagnostic Studies: Such as nerve conduction studies (NCS) and electromyography (EMG).
- Skin Biopsies or Quantitative Sudomotor Axon Reflex Testing (QSART): Used to diagnose different types of neuropathies.
ASSESSING NEUROPATHY!
Assess medical history, clinical findings, and perform appropriate laboratory tests to diagnose treatable causes of neuropathy with a slowed capillary refill rate as a standard finding.
- Evaluate by Primary Doctor to control diabetes and address other major medical issues.
Adopt an intermittent fasting program to decrease glucose and insulin dependency, and to burn fat for metabolism maintenance.
2. Local and Systemic Causes: Correct local causes like peripheral nerve entrapments (e.g., tarsal tunnel syndrome, carpal tunnel syndrome) with physical therapy, alcohol injections, or surgery.
Address systemic causes as needed.
Neuropathy Pain Treatment:
Lyrica and Gabapentin are commonly prescribed to treat neuopathy. Schreiber AK et al., in their study "Diabetic neuropathic pain: Physiopathology and treatment" (World J Diabetes. 2015 Apr 15; 6(3):714-528-3668, DOI: 714-528-3668/6.i3.432), highlight the limited success of Lyrica and Gabapentin. These medications only cover up neuropathic pain as non-narcotic pain relievers but are associated with sleep disturbances and other complications.
Nitroglycerin as an Alternative Neuropathy Treatment:
Nitroglycerin has been used for over 75 years to treat angina by improving microcirculation. Dr. Mark Reed has applied nitroglycerin patches for over 30 years to enhance blood flow in the lower extremities, effectively reducing or eliminating neuropathic burning pain. Research supports transdermal nitroglycerin as an effective treatment for neuropathy pain. (Taheri A, Farbood et al., "The effect of transdermal nitroglycerin on pain control in diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathy." J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2015 Dec 1; 14:86).
Nitroglycerin Assessment:
- Effectiveness is determined by the Capillary Refill Time (CRT) and forefoot temperature.
- The loading dose is raised over a week leading to pain relief and nerve regeneration within three to five months.
- Neuropathy reversal observed in patients with normal physiology and those with fibromyalgia or chemotherapy-induced neuropathy.
- Nitroglycerin also reverses autonomic neuropathy symptoms by providing increased capillary oxygenation to major organs (eyes, kidneys, brain).
- Lifetime regimen combined with controlled blood glucose levels helps prevent neuropathy and foot ulcers.
- Other Medications: Medications for pain management (e.g., Capsaicin, menthol liquids and creams) do not cure underlying small vessel oxygen damage but provide symptomatic relief.
PREVENTATIVE INTERVENTION
If you have Neuopathy and numbness
- Daily foot inspections
- Walk for 30 minutes with 5-minute rest intervals
- Use protective diabetic shoes with pressure-reducing insoles
- Never walk barefoot at home
- Three-month checkups with your diabetes doctor
- Bimonthly visits to a Foot Specialist
- Urgent appointments with a Foot Specialist if prominent or purple callous is observed, and limit weight bearing
- Exercise to Reduce Neuropathy Pain:
Low-Impact Exercise: Increases tissue oxygenation, reduces pain
- Gradual Introduction: Start slow and ease into the program
- Daily Goal: 30 minutes of exercise on alternating days
- Doctor Consultation: Check heart, eyes, kidneys, and feet, and discuss blood glucose levels before and after exercise
- Glucose Management: Have a glucose source available during exercise
- Recommended Low-Impact Exercises:
- Swimming
- Water aerobics
- Recumbent bicycle riding
- Rowing machine
- Yoga
Balance Exercises:
- Practice daily
- Stand on one foot for 30 seconds, alternate for ten times
- Progress to one minute on each foot for five times
- If unable to balance on one foot, lift the heel of one foot while balancing on the other for 30 seconds
- Stand on tiptoes for 30 seconds, repeat five times, and aim for one minute for five times
DISCLAIMER: MATERIAL ON THIS SITE IS BEING PROVIDED FOR EDUCATIONAL AND INFORMATION PURPOSES AND IS NOT MEANT TO REPLACE THE DIAGNOSIS OR CARE PROVIDED BY YOUR OWN MEDICAL PROFESSIONAL. This information should not be used for diagnosing or treating a health problem or disease or prescribing any medication. Visit a health care professional to proceed with any treatment for a health problem.
OC CENTER FOR WOUND HEALING & FOOT CARE
Mark Reed, DPM DABFAS FAPWCA
Open: M-F 8:30am to 5pm
Saturday: By Appointment
Email: Info@Podiatry.Care
Fax: 714-528-0739
Office: 714-528-3668
Connect with Dr. Reed